Overview
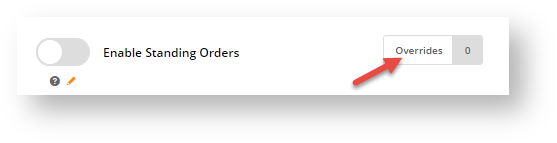
The Override facility allows Administrators to set access to a feature or function at particular levels (Customer, Role and/or User) rather than turning it on or off for all Users. It is available for a wide range of settings in the CMS. You'll know it's there if you see the Overrides button and counter next to a setting.
Example:
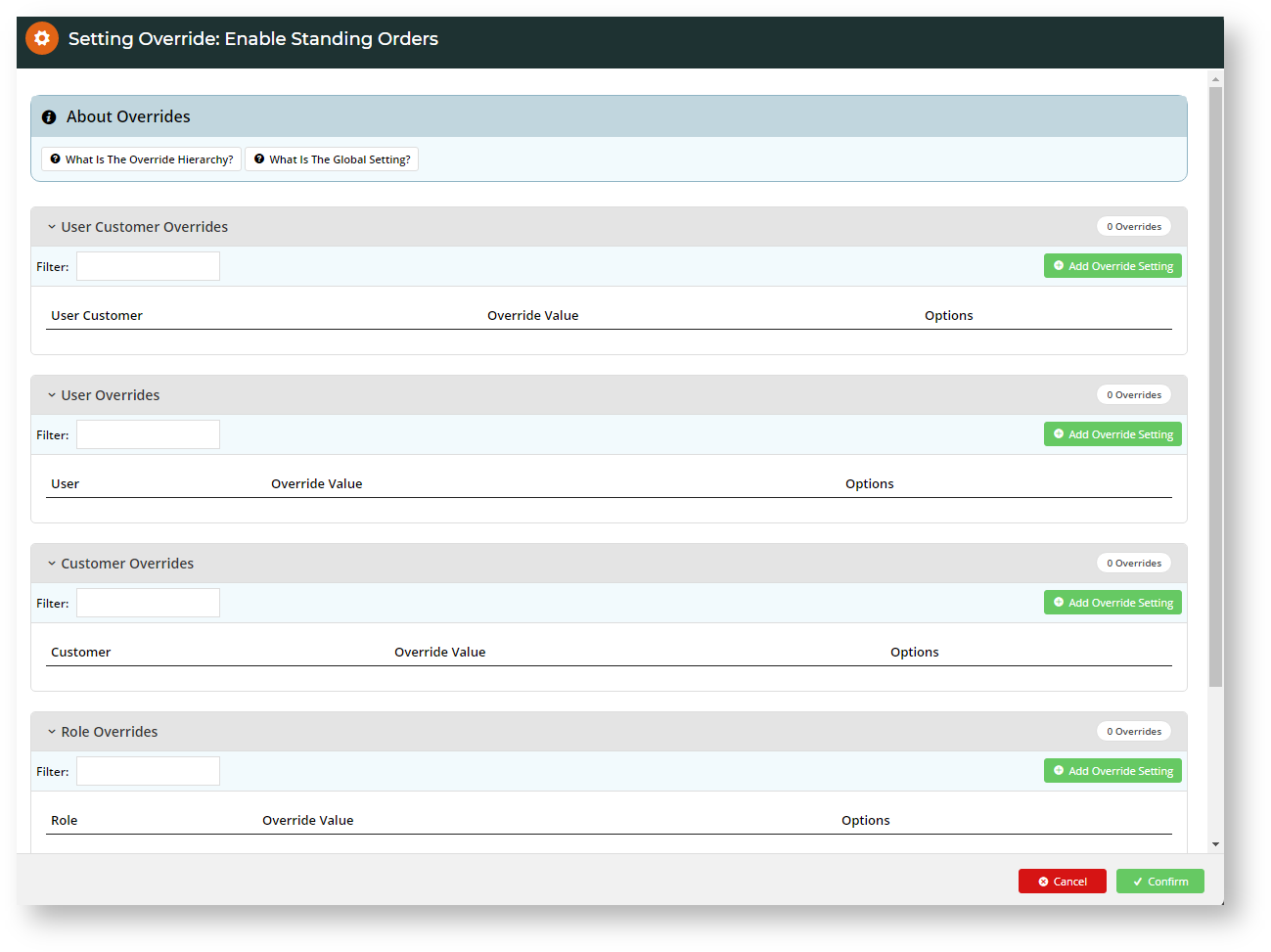
How Overrides work
Overrides takes advantage of the different levels that are set against Website Users to control access to a setting or function. There are general rules operating on levels and overrides (Global < Role < Customer < User):
- The Global level is always the fallback
- A Role level setting overrides Global.
- A Customer level setting overrides both the Role and Global settings.
- A User level overrides all previous settings.
- Sometimes you will see a User Customer level. This appears for settings where Users are in more than one Customer account on your website and allows you to set permissions for the User against a specific Customer. This level overrides all other settings.
NOTE - Sometimes, a setting will specifically allow/disallow certain levels or have rules that exclude certain subset of Users already.)
Use Case
As an example, let's use the 'Standing Orders' feature. 'Standing Orders' allows Users to create recurring orders, e.g., scheduled orders that will automatically be placed depending on the frequency set. Let's say we want to grant standing order rights to only a subset of Users - B2B buyers from specific Customer accounts. The Enable Standing Orders toggle is the global setting. If we toggle it ON with no overrides, the setting will be available all Users. If it is OFF, no User will have access. We don't want either of these and will use the Overrides facility. There is usually more than one way to achieve permissions but we have to careful how our overrides solution will affect all other Users..
For our example, the easiest way of achieving our permission goals is to leave the global setting OFF and set overrides at particular levels that apply to targetted Users. Say we have a registered user 'Jane Smith' (User) who has the Roles of B2B purchaser (CSSUser) and Accounts in the company accounts 'AACAB' (Customer) and 'WAFFA'. We want to allow her to create Standing Orders only when she is logged into the Customer account 'AACAB'.
Step 1: Leave global setting OFF.
Step 2: Click the Overrides button. This will open the Setting Overrides screen specific to the feature.
Step 3: There are various Override options we can set. Bear in mind how your override settings will affect all other Users.
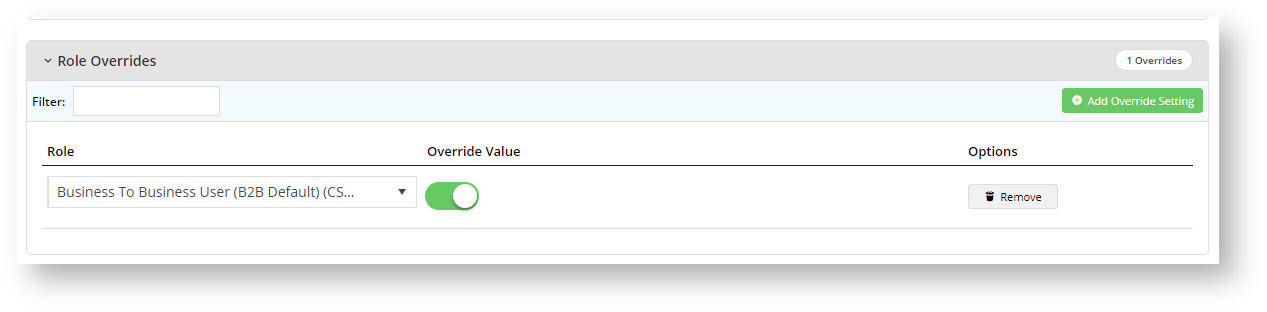
We can decide to set a Role override with an Override Value of ON. Jane will have access to Standing Orders but so will all other Users on your website with the same Role. If that is fine, then you do not have to set any other overrides. Just click Confirm, then Save your Override. If not, we can set Overrides at other levels.
Step 4: We can set Customer Overrides so that Jane in the CSSUser Role can only create a standing order when in the Customer account 'AACAB' and not in her other account 'WAFFA'. But this will affect all other Users with the CSSUser Role in the WAFFA account.
Another way is to